Glossary of Terms
in Trucking
[A] [B] [C] [D] [E] [F] [G] [H] [I] [J] [K] [L] [M] [N] [O] [P] [Q] [R] [S] [T] [U] [V] [W] [X] [Y] [Z]
Transportation professionals use their own technical language like LTL, Full Truck Load, Flatbed Trucking, etc. You may feel a bit lost, if you are new to the industry. Hope this list of common terms in the trucking industry will help you..
A
American Trucking Associations (ATA) :
ATA is founded in 1933, headquartered in Virginia. It is the largest national trade association for the trucking industry in America.

Automatic On-Board Recording Device (AOBRD) :
See Electronic On-Board Recorder (EOBR)

Accessorial charge :
It is an extra/added/supplemental service charge for what's considered beyond normal. For example, out of routine pick up and drop off, time delayed by shipper, load or unload extra freight, secure odd sized cargo to a flatbed trailer, etc. This is more frequent with LTL shipments.

Authority :
United States Department of Transportation (DOT) is the authority for both carriers and freight brokers to operate legally. See also Operating Authority

B
Backhaul :
The return trip from destination to its point of origin, which usually pays a lower rate than the headhaul.
Backload, if it's a non-paying load.
Payload, if it's a paying load.

Big-Rig :
Also called Semi-Truck

Big Truck :
Also called Semi-Truck

Bill of lading (BOL, BL, B/L) :
It is a legal document issued by a Carrier (master of the ship) to Shipper (person consigning the goods) acknowledging the receipt of goods transported. It includes type by weight, size, number of pallets or boxes, quantity, origin and destination of cargo carried. See also Manifest

Bobtailing :
Truck without a trailer attached. This happens when a truck driver first goes to pickup site. This is different from Deadheading.

Box Truck :
See Pannel Van

Broker / Truck Broker / Freight Broker :
Is the middle man who arranges transportation services. Shippers often hire brokers to find carriers. It is a flexible way to transport their goods.

Bulk Cargo :
Large quantities of loosely and unpackaged cargo. Items such as grain, oil, coal or dry powder. See Cargo

C
Cabin / Cab / Cabriolet :
This is driver's compartment of the truck located at tractor. It's a rest room for the driver with air suspension seating, sound systems and bed to sleep when tired.

Cab Over / Cab Over Engine (COE) / Flat Nose / Forward Control :
A truck body (box shape tractor) with a flat face vertical front (no bonnet). The truck cabin sits above the front steering axel and engine. See Conventional Truck

Capacity Crunch :
In trucking industry, capacity means the availability of trucks for hire to haul cargo.
Trucking Capacity Crunch means to have less truck containers and container space for freight. It makes difficult for shipper to find full truckload causing dramatic increase in pricing.

Cargo :
The materials, goods or merchandise being transported via truck for commercial gain, where receipt is issued by the carrier. Also called freight.

Carrier :
A trucking company or an individual that transports freight or cargo from one location to another. He is responsible for any possible losses of goods during transportation. See Shipper

CB radio / Citizen's Band Radio :
This short range radio communication system is used by truckers to talk to other truckers on highway, discuss road and weather conditions and in emergency situations. CB radio was first licensed in 1947. There are 40 channels in United States at frequencies from 26.965 MHz to 27.225 MHz (UHF 460 MHz to 470 MHz) with distance of 25 Km for moving trucks. Many truck drivers use CB channel 19 (27.185 MHz) known as the [highway channel] or [trucker's channel].

Combination Vehicle :
Truck consists of two or more units, Tractor and one or more Trailers.

Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) :
A must requirement to drive trucks in United States. See CDL

Common Carrier / Public Carrier :
A carrier who transports cargo for general public and responsible for any possible losses during transportation.
Term: Common Carrier is used under common law.
Term: Public Carrier is used under civil law.
See also Contract Carrier and Private Carrier

Company Driver :
An employee of a trucking company who drives trucks provided by his employer. See also Owner-Operator (O/O)

Consignee :
Consignee is the recipient (usually the buyer) of Consignment (cargo) delivered to the port of desitination by the Carrier. Formal ownership of cargo is transfered to the consignee when the payment of Consignor's (seller's) invoice is fulfilled.

Consignor :
Consignor is the person or entity sending a shipment by transferring the legal responsibility or ownership of freight (consignment) to the Carrier. See also Consignee

Consignment :
Consignment is the shipment of cargo sent by a Consignor (seller) to a named Consignee (buyer), where the Carrier (trucking company) takes responsibility for transportation.

Contract Carrier :
A for-hire carrier (commercial individual or trucking company) contracted to carry cargo, only for a certain shipper (customer). This type of carrier enters into contract after considering and negotiating the terms of shipper. Therefore, Contract Carrier has rights to choose or refuse the cargo for payment, in comparison to Common Carrier.

Contract Rate :
The rate agreed per Km for an extended term. For example: One year contract. See also Spot Market Rate

Conventional Truck :
Tractor of truck has a bonnet (hood), where the engine is in front of the cabin. See also Cab Over Engine

D
Day Cab :
A truck cab without speeping compartment. It is not indended to be used for overnight long trips, because it lacks a sleeper berth.

Deadheading :
When driving a truck pulling an empty trailer (no cargo). It happens on your way to the origin to pick up a load.

Dedicated Route :
A prescribes/assigned single regular route to a truck driver. Dedicated route truck driver can operate in a predicatable schedule.

Department of Transportation (DOT) :
DOT is the Federal agency that develops, implements and enforces regulations for interstate trucking in United States. Keeping travel safe and secure, increase mobility, and transportation system contribute to the nation's economic growth are top priorities of DOT.

Drop and hook :
When a driver leaves an empty trailer at a warehouse and hooks up to a different full trailer for the return trip. This eliminates driver's to waiting time for live loading or unloading, in turn less expensive.
Dry Van :
A truck trailer that is enclosed and protected from cargo falling. Standard dry van trailer dimensions for a dry van truck is 53 feet in length (53 ' x 8 ' 6 ” x 8 ' 6 “). A standard dry van trailer can haul up to 45,000 pounds of cargo or 26 standard pallets.

E
ELD (Electronic Logging Device) :
Earlier, this device was called Electronic on-board recorder (EOBR). In 2015, the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) introduced this new term ELD and officially replace it in December 2019.

Electronic On-Board Recorder (EOBR) :
This is an electronic device hooked to a truck. It logs and transmits the truck location, speed, and idle-time, etc. It is a cost effective alternative to traditional paper based logging. EOBR is a useful management tool, where drivers can keep detailed logs of their Hours Of Service (HOS). Now this device is called ELD (Electronic Logging Device).

Expedite freight :
Expedite freight is time sensitive. It must be delivered at a preset delivery time. Therefore it is costly for shippers and most profitable but challanging to carriers.

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) :
ERP is a real-time software used by companies to manage and integrate main business processes. It facilitates information flow across departments (Planning, Accounting, Manufacturing, Purchasing, Sales, Inventory, Marketing, Human resource, etc). A single system that integrates all processes helps to implement resource planning. It also manages connections to external stakeholders. See also Transportation Management Software (TMS)
F
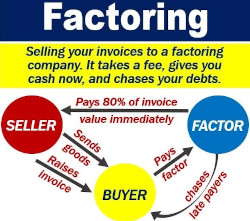
Factoring :
Before delivering a load and waiting for payment, a carrier receives payment from a third-party financial company (called factor), thereby improves cash flow. It's a type of debtor finance, where a business sells its accounts receivable to a third party at a discount (factoring company retains a percentage of carrier's earnings as it's fee).
Flatbed :
A trailer without cover/enclose part. Back/bed of the truck is flat and open and can be loaded from all sides. Also called Stake Beds. It is used to transport oversized or wide load items like heavy machinery, equipment, building supplies, etc.

Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) :
It is an agency within the USA Department of Transportation. FMCSA regulates the trucking industry in the United States by enforcing commercial motor vehicle safety regulations. It's main objective is to reduce crashes, fatalities and injuries involved with large trucks. Therefore, truck drivers are required to keep logs of their HOS (Hours Of Service) by law.

For-hire Carrier :
Truck company transports cargo for other carriers (truck companies).

Forklift :
Forklift is an industrial truck to lift and move heavy loads in a warehouse (short distance). It can safely lift objects where humans cannot. See also Pallet

Float shifting / Slip shifting / Dead sticking / bang shifting :
To change gears without using clutch pedal. Skillful drivers perform it carefully. If improperly done, it can ruin a transmission.

Full Truck Load (FTL) / Truckload shipping :
Truck is dedicated to a single load (reserved for one shipment only). This method is used when transportation takes the entire space of a Trailer, either by reaching its maximum volume or weight. Alternative is Less-Than-Truckload (LTL).
Freight :
See Cargo

Freight Broker :
An intermediary person who arranges transportation between a shipper and a carrier. Also called Property Broker

Fuel Surcharge (FSC) :
Cost of fuel is covered in this charge. It is an extra fee. Trucking companies charge it to cover the fluctuating fuel costs and add to shipper's freight bill by calculating it as a percentage of the base rate.

G
H
Hauling / Haulage :
The business of transporting goods by large trucks. See Long Haul Trucking

Hazardous Materials (Haz-Mat) :
Potentially dangerous freight (flammable, poisonous, explosive). Under Haz-Mat regulations, it is required to palcard Hazardous signs.

Headhaul :
It means truck filled with cargo heading from origin to its destination. Unlike deadheading and backhauling, headhauling is the highest paying segment of a round trip. Also called Linehaul.

Hours Of Service (HOS) :
In United States, drive time and rest periods for commercial truck drivers are regulated by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). Truck owners must ensure that truck drivers must keep, detailed logs of their HOS (Hours Of Service) by law. It reduces road accidents caused by driver fatigueness and distractions. ELD (Electronic Logging Device) is used to log and transmit HOS automatically.

HotShot :
Hotshot trucking carries relatively smaller, but time-sensitive loads to accessible locations. Instead of filling trailers with multiple loads, they generally take incomplete or Less-Than-Truckload (LTL). They dedicate their route and schedule to a single customer.

I
Invitation For Bid (IFB) / Call For Bid :
See Request for Quote (RFQ)

International Fuel Tax Agreement (IFTA) :
It is a cooperative agreement between Canadian provinces and the lower 48 states of United States, where carriers report fuel tax paid in more than one jurisdiction. Then the money is re-distributed to the provinces and states where the fuel was consumed.

Intermediary in Trucking Industry :
It refers to third party logistic company (3PL) or a freight broker acting as the facilitator to arrange transportation on behalf of a shipper. See Transportation Intermediaries Association (TIA)

Intermodal :
Same shipment of cargo is transported in many modes (Truck, Rail, Sea and Air).

Irregular Route :
Also called Over-the-road (OTR). See also Regular Route

J
Just-In-Time (JIT) :
A management practice where cargo arrives Just in time, only when needed. This inventory control method reduces or eleminates warehousing.

K
L
Lane :
A route from origin to destination.

Load-to-Truck Ratio :
=
number of available loads on the market
/
number of available trucks to carry those loads

Log book :
It's an official document (form) describing the truck driver's working duties for a period of 24 hours. It also can record the important events in management and operations.
Less-Than-Truckload (LTL) :
LTL carrier transports relatively small freight, and when cargo does not require the entire trailer. Alternatives are parcel carriers or FTL (Full Truck Load).

Linehaul :
See Headhaul

Load :
A single cargo shipment.

Long Haul :
A long journey where truck drivers spend the night away from home. They may spend the night at a motel or at their truck cabin. See also Hauling and Over-the-road

M
Manifest :
A document describing a list of cargo delivered from a warehouse. It's more descriptive than a Bill of Lading. Content of a Manifest are cargo name, quantity, origin, destination, price/cost/invoice, etc. It can be used as a checklist when unloading.
Motor Carrier :
A commercial motor vehicle use to transport cargo by a truck company.

N
O
Onboarding / Organizational Socialization :
The process of integrating a new driver or customer to the company.
Onboarding also refers to a freight broker bringing a carrier he has never worked with before.

Owner-Operator Independent Drivers Association (OOIDA) :
It is a North American international trade organization founded in 1973 and based in Missouri. It fights for the rights of truck drivers.

Operating Authority :
To engage in interstate commerce, motor carriers must register at Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). See also Authority

Oversize Load :
A unit of oversized cargo that exceeds the legally defined maximum length, width and/or height, with few exceptions require a state permit to travel on public roads and highways.

Over-the-road (OTR) :
Long Haul truck drivers who transport cargo over long distances do not follow the same schedule and same route everyday. They spend weeks and months away cross-country. Also, Common Carrier drivers day to day serve different clients, and transport goods without prescribed routes and schedules. They can shift from Less Than Truckload (LTL) to Full Truckload (FTL) and so on, based on shipper requirements. Also called Irregular Route.

Owner-Operator (O/O) :
A small business owner drives his truck on regular basis. He may lease his truck to a larger carrier company and drive under that carrier's authority. See also Company Driver

P
Pallet :
A flat wooden or plastic platform structure that heavy goods are stable stacked to be lifted by a pallet jack or a forklift truck.


Pallet Jack :
It is a tool to lift and move pallets within a wearhouse. A basic form and an alternative to a forklift. See also Pallet.

Pannel Van :
There are various sizes of pannel vans. Some are small as mini vans and some have fairly large boxes at the bed of trucks. Also called Box Truck.

Parcel Carrier :
Delivery in containers, parcels, or high value mail as single shipments. There are different sizes, shapes and weights for parcels. Parcel carrier service is provided by private courier companies, most postal systems, express mail and Less-Than-Truckload (LTL) shipping carriers.

Power Only :
Shipper has the trailer. Therefore he may only request a power unit (Tractor) to pull the trailer.

Power unit :
Truck has tractor and trailer. Tractor has the power engine.

Private Carrier :
A shipper company owned truck used to transport its own cargo. It does not offer transportation to general public (not-for-hire). Not required by law to register at Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). See also Common Carrier

Property Broker :
See Freight Broker

Q
R
Regional Route :
Regional routes such as SouthEast, MidWest are limited geographical regions where a driver transports goods. Since the distance is withing a certain radius of the trucking company, drivers stay home more frequently.
Regular Route :
Same as Dedicated Route. See also Irregular Route

Rate Per Mile (RPM) :
Total price = Rate per mile (include fuel surcharge) X number of miles.
RPM pricing is used in Spot Market.

Receiver :
The party who is financially responsible for receiving a shipment as the name in bill of lading. He may or may not be same as buyer, importer, consignee.

Reefer :
It is a truck or tailer wich has a refrigerated unit and a thermostat to transport perishables and temperature sensitive goods. They are also called chiller trucks. See also Refrigerated Container

Refrigerated Container :
It is an insulated enclosed trailer with a stand alone engine mounted underside or front of the trailer, where it cools the cargo down to -40F to -45F. See also Reefer

Request for Proposal (RFP) :
A company document to announce details of a project (Example: procurement of product or service). It solicits potential suppliers to submit business proposals. Then, the company will review the bids to examine feasibility and the bidders ability to fulfill the proposal.

Request for Quote (RFQ) :
It is a business process, where a company solicits selected suppliers / contractors to submit price quotes. It is an Invitation For Bid (IFB) / Call For Bid.

S
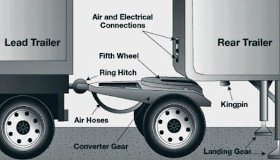
Semi-Truck / Semi-Trailer Truck / Articulated Truck / Big-Rig :
It is a jointed (articulated) 18-wheeler truck, a combination vehicle of tractor and trailer to carry cargo. The tractor's front axle/hitch is for assembly is called a dolly/fifth-wheel. Most of the load is carried by the trailer. A trailer without front axle is called a semi-trailer. It has legs to to support when unhooked from the tractor.


Shipment :
Physical process of transporting (shipping) cargo.

Shipper :
Is the sender (person or company for example: manufacturer, distributor, retailer or grower), usually the supplier or owner of commodities shipped. Also called Consignor, Exporter, Seller. See also Carrier

Sleeper Berth (Bed) :
A truck cabin contains a bed (berth) where the truck driver can sleep when taking breaks.
See also Day Cab.

Spot Market Rate :
Spot market freight rate is determined by short-term supply and demand conditions. It is not a long-term contract between carrier and shipper. See also Contract Rate

Super Single :
A large wheel & tire (wide-base tire) instead of duals. Benefits are weight reduction and less fuel economy because of lower rolling resistance on road. Disadvantages of super single tire compared to dual tyres are lack or tire redundancy (critical when tire blows out) and road surface scrubs when making tight turns. Eighteen wheeler dual tire conventional truck supports only ten super single tires because of improved design.


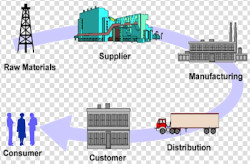
Supply Chain Management (SCM) :
It is management of the flow of goods and services including processes from point of origin to the point of consumption. It involves storage and movement of raw materials, inventory of work-in-process and finished goods. SCM gives competitive advantage to the company in the marketplace. Transportation / Logistics is a key element in SCM. See also Transportation Management Software (TMS)
T
Tandem Axle :
Two or more axles one behind the other. USDOT legally defines, axles should be spaced between 40 inches and 96 inches. At higher speeds, truck is more stable and can handle more weight of cargo because of extra tires.

Truckload Carriers Association (TCA) :
Truckload carriers formed this national trade association. TCA is based in Virginia. See Carrier

Team Drivers :
A team of two or more drivers shift turns in driving the same truck. Advantages are less break time and fewer stops resulting long hours on road (more miles). Having an extra person in the cabin spends quality time in driving. Shipper pays more for time-sensitive cargo.

Terminal :
A processing node.
See Truck Terminal.

Tractor :
Front part of a truck that pulls the Trailer.

Tractor-Trailer :
Also called Semi-Truck.

Trailer :
It is the non-motorized rear unit of a truck towed by a powered Tractor. Flatbeds, Dry Vans and Reefers (Refrigerated units) are common trailer types.

Truck :
Truck is a 18-wheeler vehicle, a combination of Tractor and a detachable Trailer.

Truckload :
See Full Truck Load (FTL).

Truck Stop Electrification (TSE) :
It is a technology where Truck Stop Locations provision land-based electrical power (Shore power) to trucks via a hose attached to the window. It provides heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAL). It eliminate the need for truck engine idling while parked. Also facilitates Internet and TV access.

Truck Terminal :
A dock or hub where a trucking company is based, receiving and dispersing items for delivery. Or it can simply be a place where cargo originates, terminates and handled for transportation. Or an operating facility where mortor carriers maintain.
See Terminal.

Transportation Intermediaries Association (TIA) :
A trucking industry association for third-party logistics professionals (3PLs) and freight brokers. It is based in Virginia. See Intermediary

Transportation Management Software (TMS) :
A computer software designed for the transportation industry. It considers Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP).